Governance and Economic Dimension
Sustainability

Central Pattana Public Company Limited are committed to operate our business with transparency, morality, ethics, and due regard for the balanced interests among stakeholders, which would pave the way for long-term stability and growth in tandem with a healthy society and environment, guided through the years by a Code of Conduct and a Corporate Governance Policy which all personnel have consistently complied.
Code of Business Conduct
The Code of Business Conduct provides good practices for CPN employees to apply to their jobs so that business execution may prove transparent, moral, and ethical, with due regard for all stakeholders. The Company has therefore defined a Code of Conduct Handbook as a guideline to which directors, executives and employees shall adhere, as follows:
Code of Conduct and Corporate Governance Principles
Code of Conduct for Suppliers
Governance and Economic Dimension
Enterprise Risk Management
Target
Review, monitor, and develop the Key Risk Plan of the company every quarter.
Management Approach
- Utilize customer satisfaction assessment data to enhance and improve quality in product, service, and operational processes.
- Innovate customer experiences through collaborations with both domestic and international partners.
- Develop the project into a "Center of Life," transforming the shopping center beyond retail by creating Shared Value (CSV) that addresses genuine societal needs and benefits the community, following a Mixed-Use approach to enhance the value of visiting.
Governance and Compliance
Target
No legal disputes, convictions, complaints, or claims have been filed or raised regarding environmental, social, and governance matters against the company.
Management Approach
- Treat all shareholders equally and fairly, especially during the annual shareholders' meeting, where each shareholder has the right to vote proportionally to their shareholding. The company provides information both before and after the meeting following the guidelines of the securities market and regulatory authorities.
- Participate in the "Opportunity Day" organized by the stock exchange every quarter to present business information and operations, engage with investors, and gather feedback from shareholders and investors.
- Monitor performance through Objective and Key Results (OKR) indicators, reporting to the management team quarterly to track operational progress, push policy initiatives, and support achieving organizational goals.
Read more about Policies & Implementing guidelines
Product & Service Quality
Target
There have been no complaints regarding products and services that have impacted health and safety, nor have there been any violations of the law.
Management Approach
- Incorporate Green Building guidelines for energy efficiency and environmental friendliness into project design and development, adhering to sustainability and operational standards such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems, ISO 14064-1 for greenhouse gas management, and ISO 50001 for energy management systems.
- Promote the installation of solar roofs to increase alternative energy usage and efficient energy management.
- Reduce energy consumption, emissions, and greenhouse gases through operational practices, emphasizing the selection of low-carbon construction materials and processes to minimize embodied carbon.
- Track and report the organization's carbon footprint regularly to identify continuous emission reduction strategies.
- Ensure lawful construction practices with considerations for Social Impact Assessment (SIA) and Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), while prioritizing green spaces.
- Develop projects with a comprehensive and diverse merchandising mix, efficient management practices, and sustainable support for retailers, including online platforms, to meet customer needs responsibly and sustainably.
- Conduct marketing and public relations activities responsibly to enhance project value, create community engagement spaces, and elevate the products and businesses within the community.
- Utilize knowledge, new technologies, and partnerships to enhance product and service efficiency, focusing on security systems, cleanliness, and resource management to elevate management standards aligned with circular economy principles.
Innovation Management
Target
Utilizing cutting-edge technology and innovative solutions to design inclusive experiences for marginalized communities, with a focus on consistently enhancing the quality of products and services year-round.
Management Approach
- Gather customer feedback, ideas, and pain points to improve products and services.
- Monitor global trends, innovations, and collaborations with business partners to align with company goals and strategies.
- Identify innovations that promote net greenhouse gas emissions reduction as a priority, alongside knowledge acquisition and collaboration with government entities to create positive impacts on communities, society, and the country following the BCG Model.
- Foster an innovation culture throughout the organization through projects like "Dream Team" and "Dream Big," encouraging participation in creating innovations related to individual responsibilities and operational needs. Provide continuous innovation training to keep employees updated on trends and work within the framework of Design Thinking.
- Track the continuous value of innovations, including cost savings, improved service speed, customer satisfaction, and public benefit accessibility, to guide ongoing development strategies.
Supply Chain Management
Target
- All business partners have undergone a 100% evaluation of their ESG policies.
- Conducted a 100% risk-focused assessment at the business premises for key partners.
- Enhancing the efficiency of 40 business partners per year
Management Approach
- Establish procurement and contracting policies, ethics, and guidelines for dealing with business partners, referencing regulatory frameworks and standards at national, regional, and international levels such as labor protection laws, United Nations Global Compact (UNGC), Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), and International Labor Organization (ILO).
- Integrate sustainability aspects into collaborative operations with business partners through effective communication of company expectations during selection and contracting processes. Assess partner risks alongside monitoring and evaluating performance, while supporting sustainable business practices that create shared value for society, communities, and the environment.
- Categorize business partners based on expenditure analysis, product or service importance in procurement, partner dependency levels, market leadership in product/service offerings, strategic partnership status, and develop risk management plans within the supply chain.
IT Security, Cybersecurity and Personal Data Protection
Target
Maintain a zero-record of customer privacy violations, data leaks, or losses, and ensure no reported impacts from privacy breaches on stakeholders.
Management Approach
- Develop and enhance information security management systems using ISO 27001:2013 and NIST SP800-53 standards as frameworks, covering data and information system security for hardware, software, and network systems of the company.
- Collect and manage customer databases with strict adherence to data security and privacy policies in compliance with the Personal Data Protection Act of 2019.
- Seek permission for collecting, storing, using, and transmitting personal data appropriately, including defining practices that support data owner rights and implementing measures for managing incidents related to personal data effectively and rigorously.
- Educate and raise awareness among employees throughout the organization about cybersecurity threats and their cyber impacts regularly. Plan and develop information technology knowledge for executives and board members according to appropriate development frameworks continuously.
- Obtain cyber insurance to transfer risks and mitigate potential impacts. Conduct continuous business continuity planning (BCP) exercises to handle incidents appropriately in line with the current environmental and system capabilities.
- Establish the topic of "Cybersecurity and Personal Data Protection" as one of the key risk indicators for the board of directors. Develop plans, report on operational outcomes, and allocate resources to manage cybersecurity risks seriously.
- Form an "IT Security" team to plan and roadmap continuous improvements in cybersecurity effectiveness. Collaborate with teams under the management of the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) of the Central Group.
- Recruit board members with expertise and experience in information technology to a suitable number, aligning with the company's growth directions and strategies.
Risk Management
Risk Governance
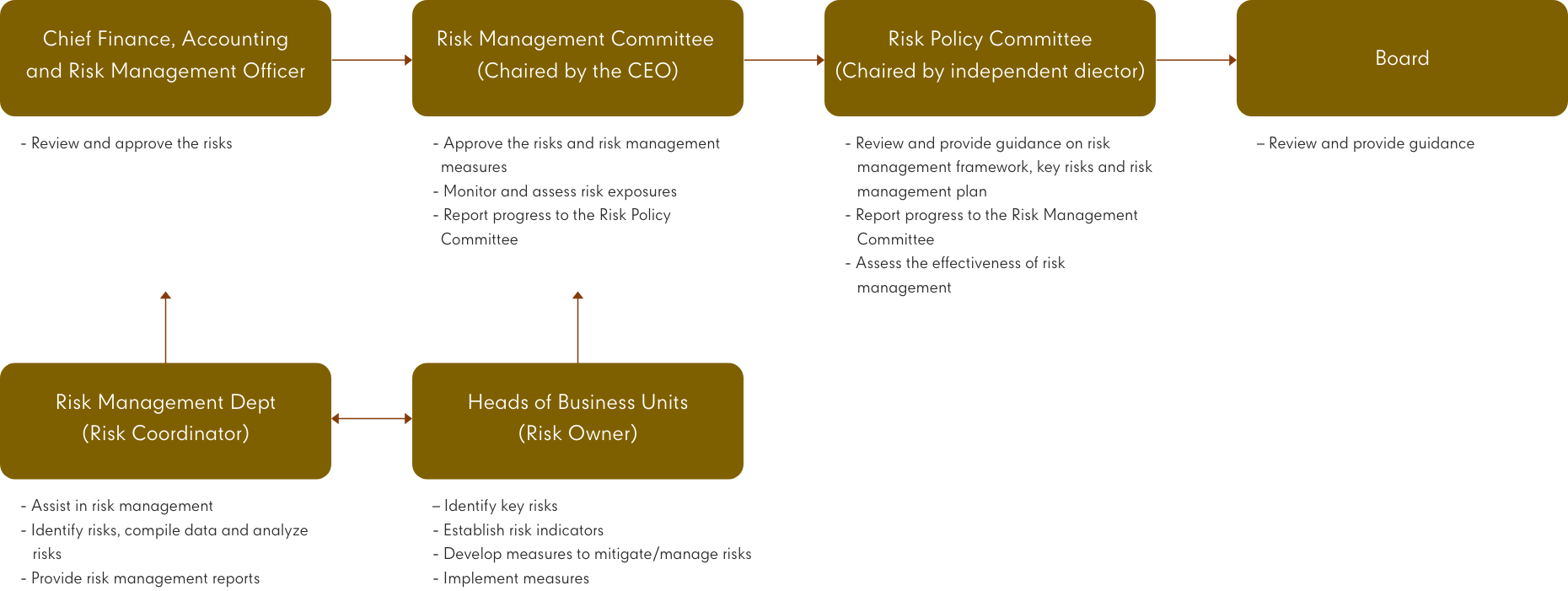
- Central Pattana ensures effective risk governance by establishing a comprehensive risk policy, setting clear guidelines for risk appetite and implementing a robust risk management framework. The roles of risk management and internal control are distinct and operate autonomously. Central Pattana assigns the responsibility for overseeing and managing risk to the following committees and executive management.
- The Risk Policy Committee, chaired by an independent director and comprising the Board and CEO, is responsible for the following: being informed on matters that are within its scope of authority and responsibility and making recommendations on the risk policy, risk management structure and framework, and the key risks that the organization faces; reviewing and approving the organization's risk appetite and tolerance; monitoring and overseeing the establishment of performance metrics and targets, and key risk indicators; reviewing and assessing the effectiveness and efficiency of management’s enterprise risk responses; and periodically reporting risk management activities to the Board of Directors.
- At the management level, the Risk Management Committee, chaired by the CEO and comprising executive and non-executive directors, is responsible for the following: overseeing the implementation of risk policy and risk management guidelines; ensuring that all business units within the organization have identified, assessed, mitigated or managed, and reported the risks that have the potential to affect the achievement of the organization's objectives and integrated risk management into its business plan with periodic progress reporting; providing support and guidance on enterprise-wide risk management activities; and periodically presenting risk management reports to the Risk Policy Committee and the Board.
- In order to facilitate the Risk Management function, the Risk Management Department, acting as the Secretary of the Risk Management Committee, is responsible for tracking, analyzing and reporting risks to the Risk Management Committee and assisting risk owners in identifying key risks and collaborating with them to assess potential exposure and develop appropriate measures to address and manage the risks to acceptable levels. The Risk Management Department reports to the Chief Finance, Accounting and Risk Management Officer.
- The Risk Management Department is responsible for assisting Internal Control in verification of critical activities across the organization in consideration of the risk exposure and operations of each business unit; and utilizing the findings and insights from internal control reports to identify and analyze key risks affecting the organization. The Risk Management Department is also tasked with providing a risk management report to the Audit Committee at least twice a year.
- The diagram below outlines Central Pattana’s Risk Governance Structure.
Risk Management Process
- The following diagram summarizes Central Pattana’s risk management framework, which is in alignment with the COSO ERM 2017.
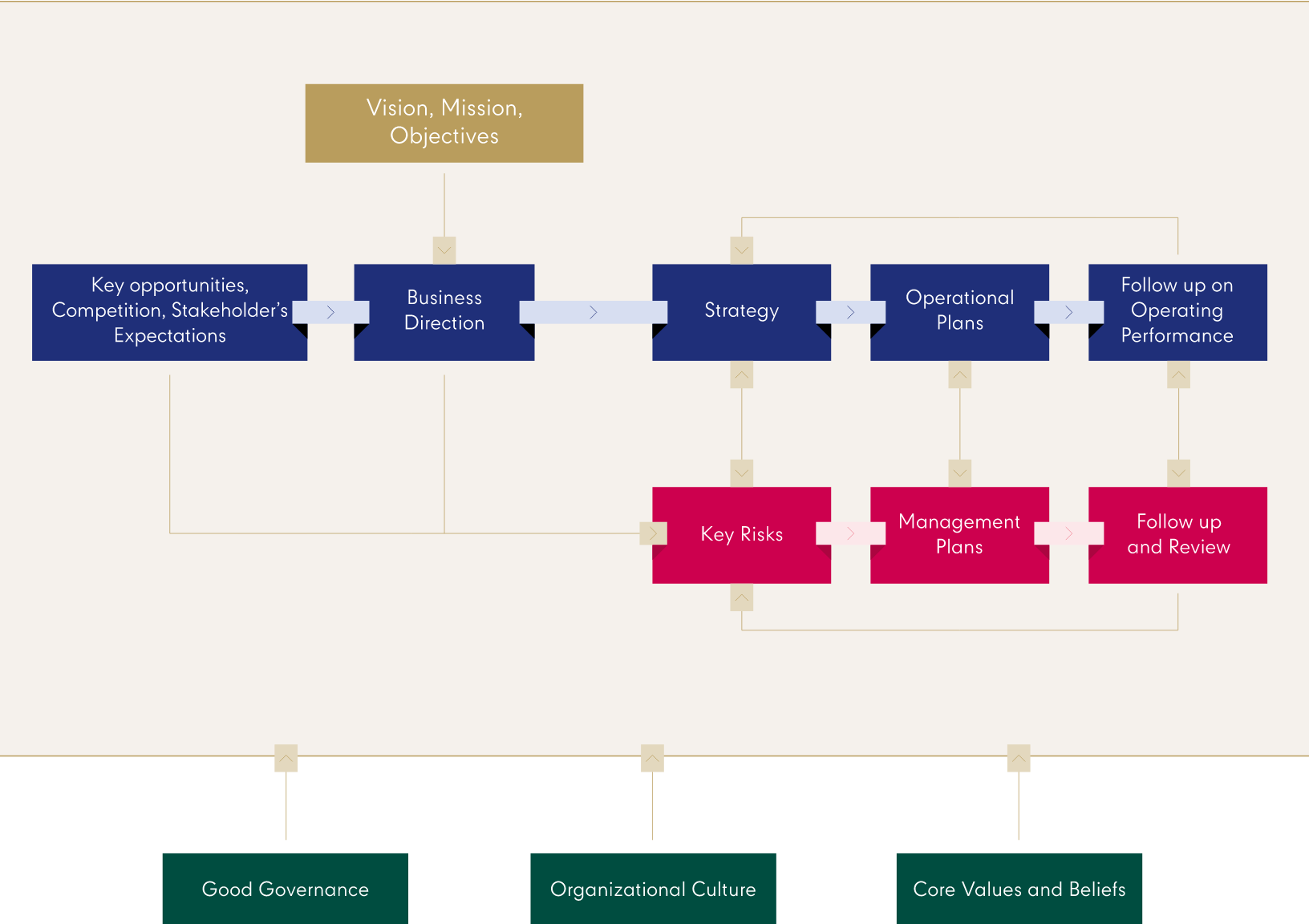
- Central Pattana conducts a thorough review of the organization's key risks and risk appetite on an annual basis and whenever there is a significant change that could potentially affect the organization's ability to compete effectively.
- To ensure alignment with the company's business direction and strategy, our risk identification process encompasses both internal and external factors. We assess potential opportunities and consider events that could impact the business, whether directly or indirectly. Following the identification of risks and opportunities, we employ a risk map to prioritize them based on their significance. This prioritization guides us in developing a risk management plan, enabling us to effectively monitor and manage the identified risks to levels deemed acceptable.
- To review the risk exposure on a quarterly basis, we use Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) to track and monitor key risks and assess the progress against the established risk management plan. The results of these assessments are compiled into reports that are presented to both the Risk Management Committee and the Risk Policy Committee.
- We regularly run sensitivity analyses and stress tests to analyze both financial and non-financial risks in which a range of scenarios such as rising wages, increasing electricity costs and regional droughts, is evaluated so that we can better understand the potential impacts and risks to our economic performance and business operations.
- The risk management process undergoes periodic audits and verifications (at least once in two years) by Internal Audit, which evaluate the effectiveness of the company's risk management practices and, where appropriate, make improvements and corrective actions.
Emerging Risks
- Central Pattana maintains a continuous monitoring and assessment process to evaluate the impact of any emerging risks that may arise. This ongoing monitoring allows us to update our risk responses in a timely manner, ensuring that they remain effective and aligned with the changing risk landscape. The emerging risks we identified are summarized in the table below.
Topic Category Description Impact Mitigation action Climate change and Its impact on El Nino Environmental In early 2023, NOAA forecasted a transition from La Niña to a strong El Niño by mid-2023. This is expected to intensify the effects of climate change, causing more frequent and severe heat waves, storms, floods, and droughts, particularly across the Pacific Ocean. This is likely to exacerbate the impacts of climate change globally, resulting in more heat waves, storms, floods and droughts especially across the Pacific Ocean, where rising temperatures could exceed 2°C on the equator. As a result, Asia and Australia may face hotter conditions and more severe droughts. With this El Niño event expected to surpass the 2016 occurrence, which saw global temperatures reach record highs, Thailand is likely to experience more intense heat waves and prolonged periods of droughts, with 29 provinces particularly those in the northern and northeastern regions at risk of water shortages, along with worsening air quality and PM2.5 pollution. - Global Climate Effects: Increased global temperatures, especially on the equator, could exceed 2°C, affecting Asia and Australia with more severe droughts and heat waves.
- Water Scarcity: For businesses, particularly those with properties in high-risk areas, the potential for water scarcity could lead to significant financial losses and increased operational costs.
- Air Quality Issues: Higher concentrations of PM2.5 due to heat and drought could affect public health, increase regulatory costs, and necessitate additional property maintenance.
Water Efficiency Measures: Implementing water-efficient fixtures, optimizing wastewater treatment and recycling systems, and maintaining strong relationships with water suppliers to manage drought conditions. Air Quality Management: Installing air quality monitors and purifiers, suspending activities that generate dust, raising awareness to reduce pollution, and piloting new technologies to lower PM2.5 levels.
Environmental Regulatory and Legislative Change Environmental The increasing unpredictability of climate change has prompted countries, including Thailand, to enhance their environmental regulations and legislative measures. Thailand aims to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 and net zero emissions by 2065, driving the introduction of new environmental laws such as the Climate Change Act, Thailand Taxonomy, and IFRS. Failure to comply with these new regulations can result in increased costs due to fines, potential reputational damage, and loss of stakeholder confidence. Non-compliance can also disrupt business operations and lead to financial and legal consequences. Proactive steps have been taken, such as establishing the Climate Change and Environment Committee (CEC) under the Corporate Governance and Sustainable Development Committee. This committee monitors regulatory changes, conducts comprehensive studies, and implements necessary standards and improvements to ensure compliance with new laws and regulations. Under supervision of CEC, the Company had developed mitigation strategy for this risk which describes in 2024_Central Pattana_AR_56-1_One Report 2023.pdf page 154-.161. under "Climate adaption"
Risk Culture
Central Pattana fosters a corporate risk culture through a range of methods, tools and channels including:
- Awareness Utilize various channels and formats to raise awareness about key risks by, for instance, distributing communication products via email and Workplace that provide information on cyber risks and the importance of data privacy and compliance with regulations like the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA).
- Training Provide online training courses to all employees on topics including risk management and crisis management and organize workshops specifically tailored for key functions such as general managers.
- Drills and Tests Conduct periodic crisis management drills to simulate different scenarios such as fires, sabotage incidents and falls from height and carry out regular business continuity plan testing for instance information security at least once a year.
- Establish ‘risk’ as one of the metrics for measuring employee performance. For example, in the case of Loss Prevention staff, their performance evaluation also includes specific criteria related to incident and crisis management.
- Communicate with stakeholders regarding key risks and their impacts, risk management measures and controls in place, and emerging risks through One Report to ensure they have a thorough understanding of the organization’s risk landscape.


